Collaboators: University of Tokyo, Japan
This exhibition design is based on three science programs Cyber Forest (1995 – present), Fukushima Base Camp, (2012 – present) and new research on the prevention of Animal Poaching, 2024 at the University of Tokyo, Japan. Each program uses human computer biosphere interaction (HCBI) strategies to collect and process audio and visual data from locations in Japan.
In 2024, we worked with Haoran Hong and Hanting Yang from the Kobayashi Lab, University of Tokyo, Chiba, Japan. They built models to show how audio data collected from the wild could be visualized in an new art science collaboration with non-human actors.
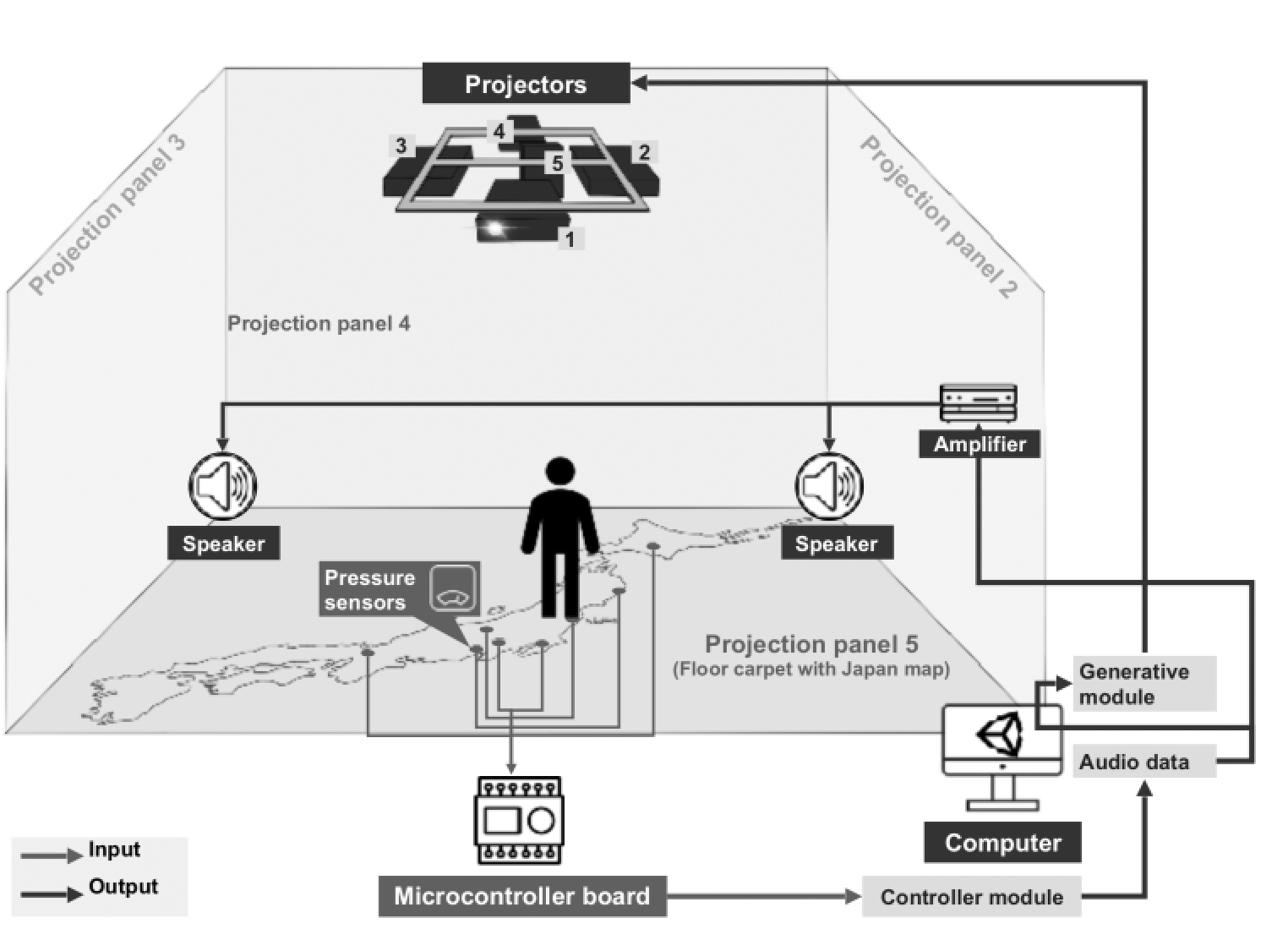
In the images below (left) Haoran Hong illustrates how the background forest imagery is muted while the isolated bird sound amplifies the colour bird visualization. (right) Haoran Hong illustrates the technology design of the exhibition.

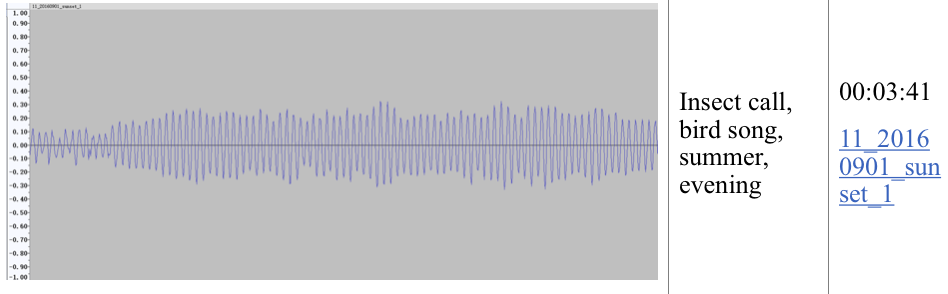
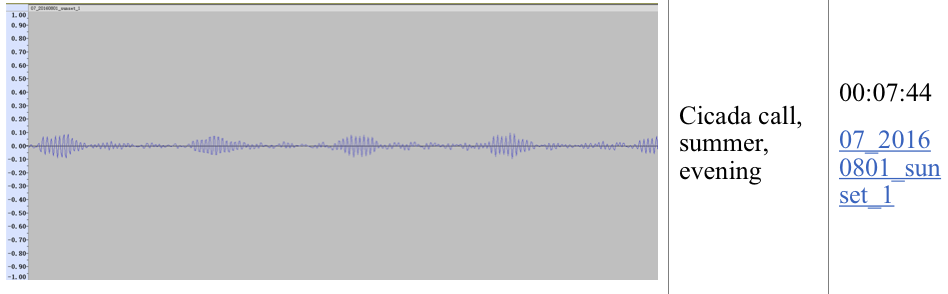
| Hanting Yang has provided examples of isolated insect and bird calls. First the forest data collected is pre-processing removing alot of the ambient sound. Than the data scientists perform some analysis tasks such as sound classification and event detection. For instance, Hanting Yang can use machine learning models to classify different types of sounds (e.g., bird calls, insect sounds), and detect and log specific events of interest (e.g., animal movements). This research is mostly done in Python using some necessary libraries or frameworks such as PyDub, SciPy, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, etc. |